|
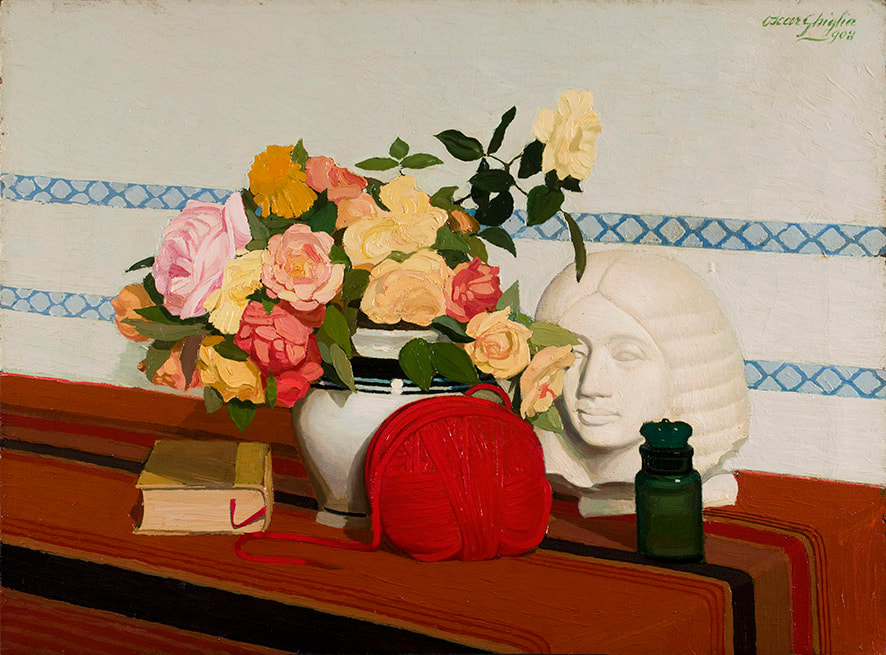
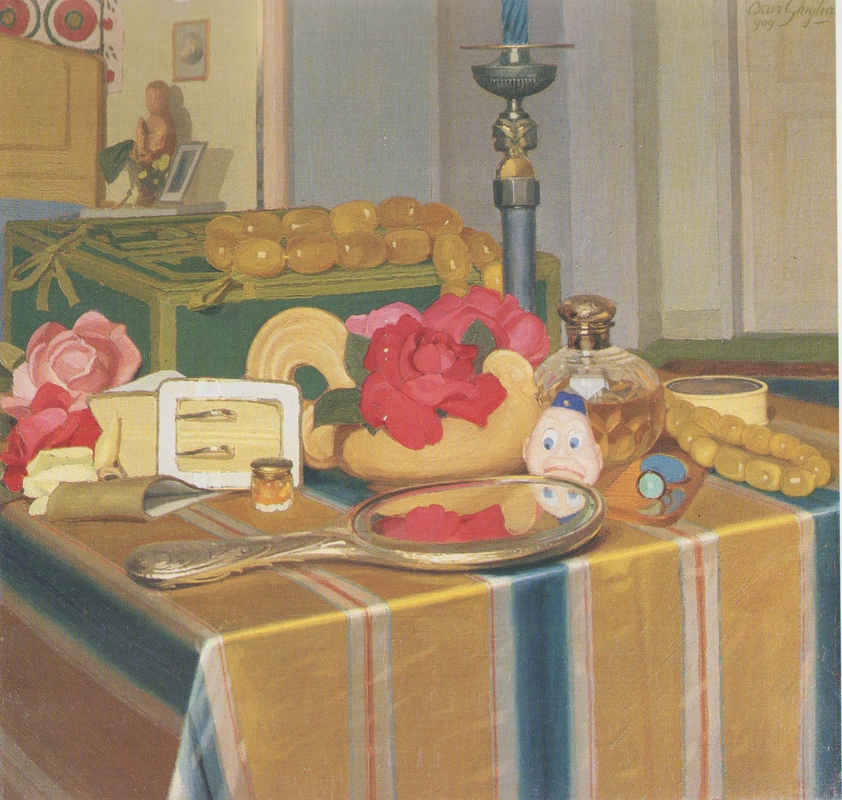
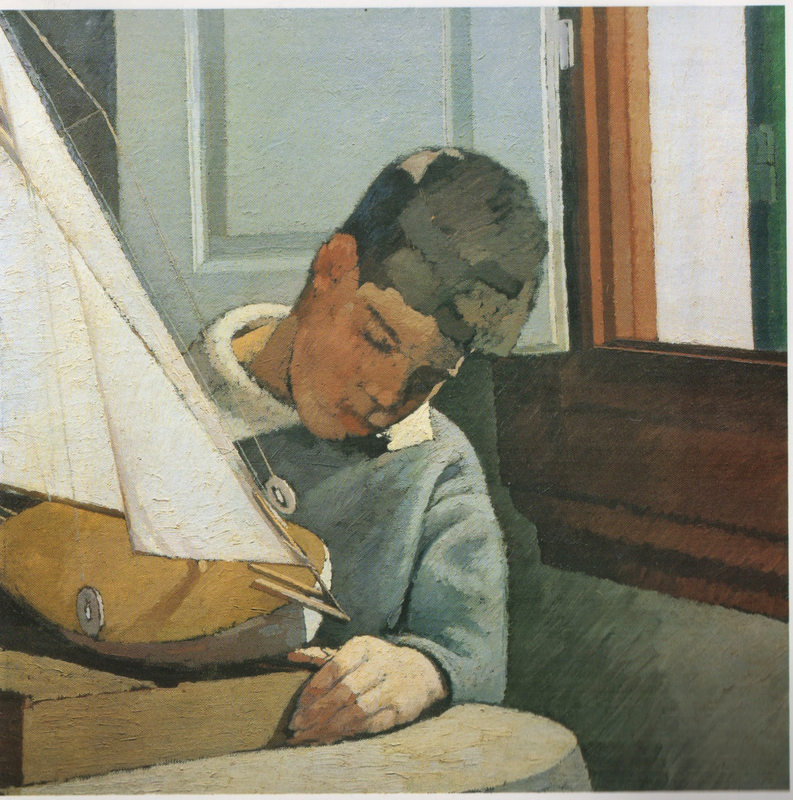
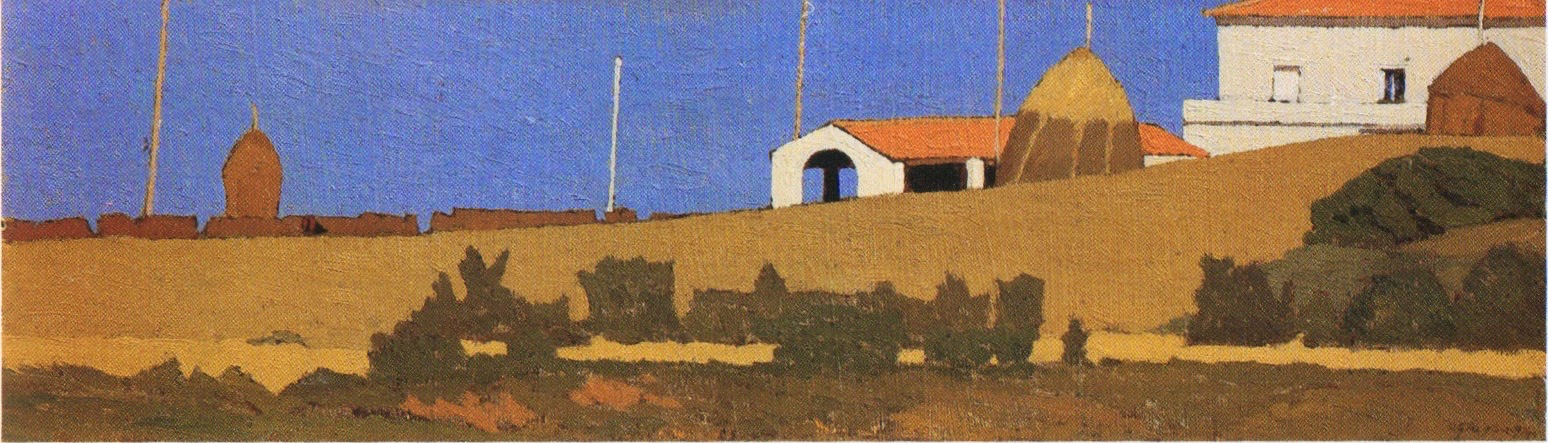
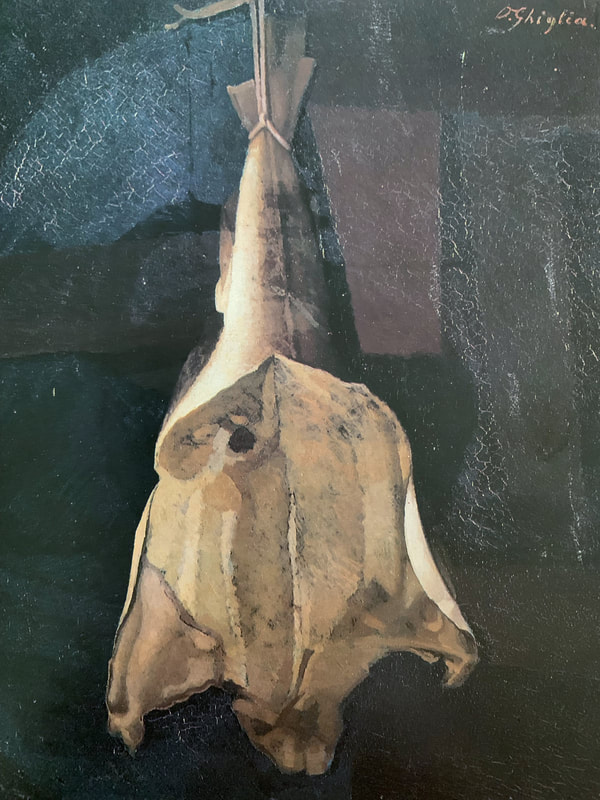
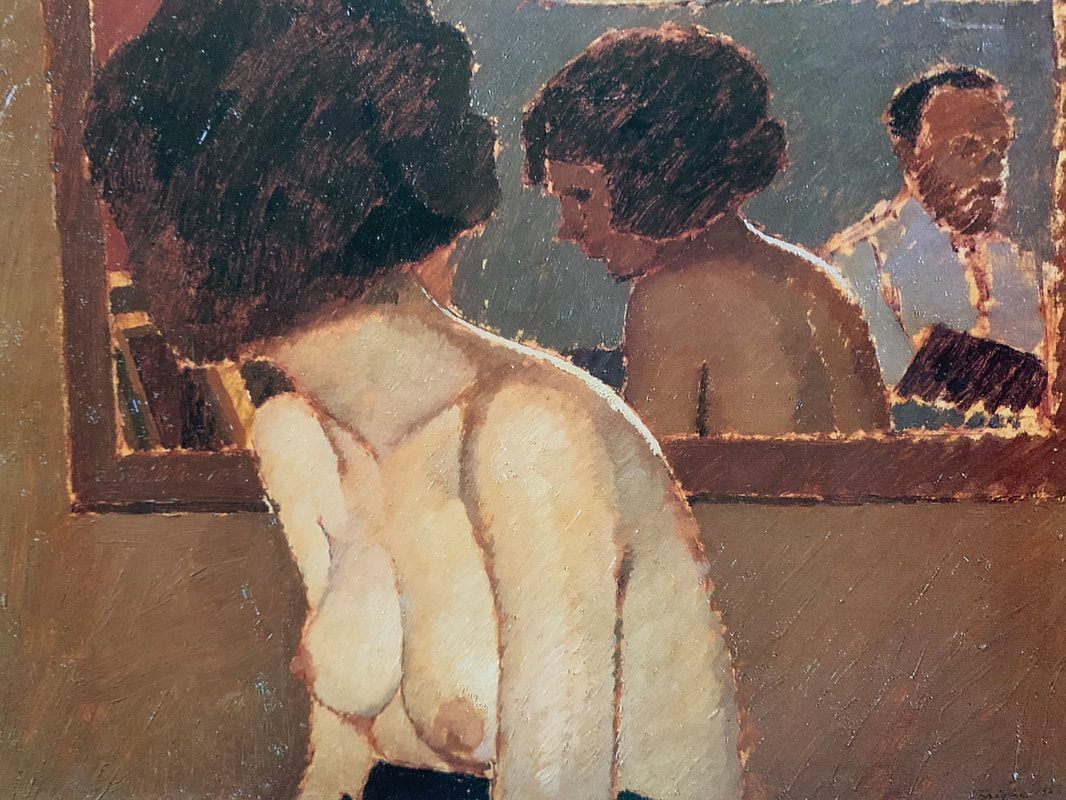
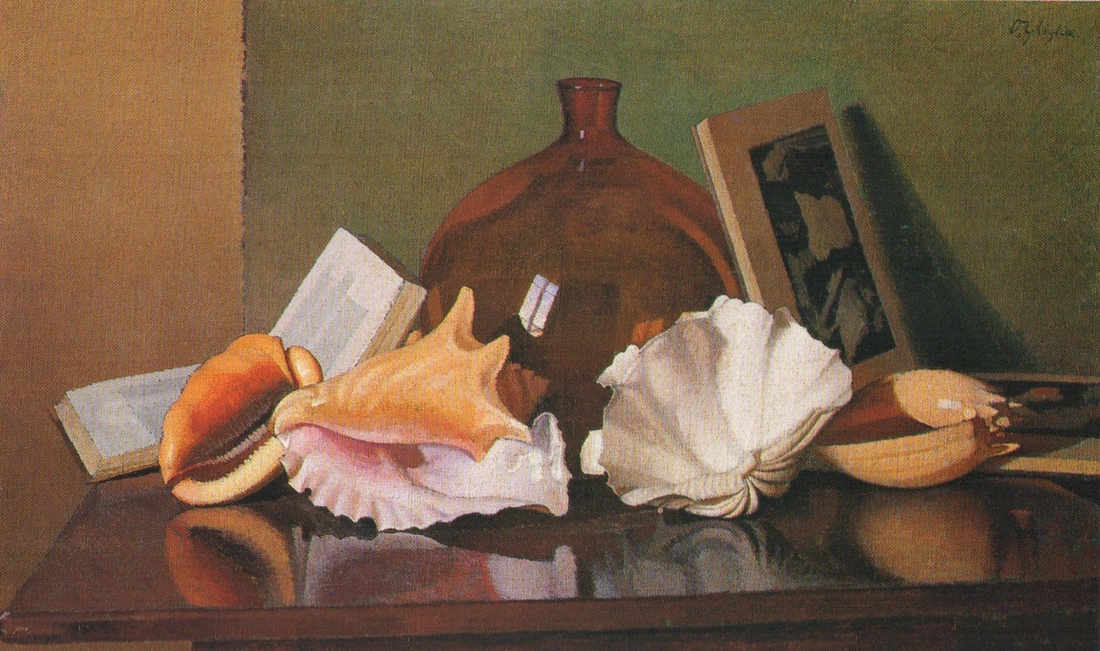
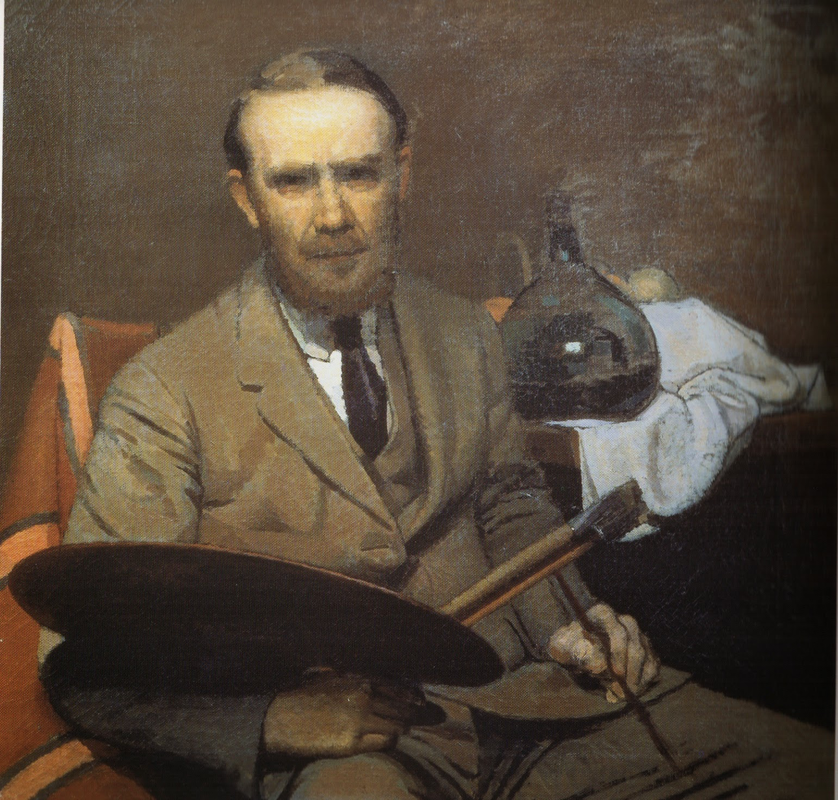
Oscar Ghiglia, A Forgotten Master I came across the work of Oscar Ghiglia in a visit to the museum of Villa Mimbelli in Livorno years ago. Since then I never had enough of looking at his work. Oscar Ghiglia, b.1876, came from a very poor family in Tuscany and lived in poverty for most of his life. He was self taught and started painting in his early youth while doing all sorts of odd jobs. In those years he lived in Livorno, a city on the Tuscan coast. Ghiglia was able to bravely overcome his humble origins and his lack of formal education, and became part of the cultural elite of Tuscany. He wrote that his sordid existance of the first years of his life "is when my character was being delineated, in that I always believed best to communicate with objects than people"- as an explanation for his love of the still life genre. In his youth he befriended the painter Llewellyn Lloyd and Modigliani, who was a little younger and from a very different background. Through Modigliani he came in contact with many jewish families to whom he was close and loyal for the rest of his life, including during the hard years of racial persecution. It was not until 1901 that he moved to Florence and started attending the Scuola del Nudo, led by painter Giovanni Fattori, the star painter of the time. Fattori respected him as an artist and they paid each other studio visits, but Ghiglia did not fully belong to his students' group nor ever ascribed to the divisionist painting language that many Tuscan painter were adopting. In Florence he also joined a group of intellectuals that included Papini and Prezzolini, who will eventually form the core of the Futurists. He was well aware of the social and political situation at the time however his art was deliberately apolitic, and he disliked the -isms of that time. He did not share the fascination for modern machines and speed that was at the core of Futurism, and later on openly condemned fascism and war. Another vital meeting of the end of the century was with his wife Isa: her devotion and affection supported him throughout his life providing the serene atmosphere that is so well depicted in his paintings. Ghiglia's artistic breakthrough happend in 1901 when his self portrait was included in the prestigious Esposizione Universale in Venice. In the meantime he was making real progress, studying the old masters preferring Titian and Rembrandt to the Florentines. His portraits are characterised by a solid perspective structure, immediate but in fact very complex. They never indulge toward sentimentality nor they become flamboyant. With a classical departure point, they are made modern by the simplification of the drawing; all the emotional content is reduced to a precise construction of the image. At the start of his career he mainly painted portraits but in the painting of his friend Lloyd ( above) his interest for still life is starting to appear. In these first years there is no evidence of contacts with European contemporary painting, particularly with artists who had interest in the domestic such as the Nabi or Scandinavian, nor William Nicholson, who were all shown in Venice too. At this stage his development was completely autonomous- although the friendship with Ojetti soon gave him access to the extensive library of this well-known intellectua, and Cezanne's influence can be clearly seen after 1910. In 1914 at the start of WW1 he finds a refuge on the coastal town of Castiglioncello with Isa and their five children. He experiences strong feelings of isolation, as he was seen almost as a bolshevic by the bourgeois holiday makers and far from the warmongering spirit of his frends, the Futurists. Here he will paint some beautiful landscapes that are integral to his work. The format and the subjects recall the Macchiaioli painters but landscape for him is in fact a rational construction. with solid brushwork, the opposite of "optical" impressionism, and an intuition of the surface as the field of chromatic relationships - like a mosaic ( in his own words). In Castiglioncello he will also paint still life and beautiful portraits such as Paulo with the Boat, above. After the war he goes back to Florence, where he witnesses with spite the rise of fascism. Figure comes back into his work, particularly the figure in the mirror, an object that will remain a favourite motif for the next decade. This period sees the resolution of his contract with the collector Gustavo Sforni, who had basically acquired the greatest bulk of his production. It was a relationship that helped him out financially for years but might have ultimately damaged the chances of his paintings circulating more widely. Now in his fifties and increasingly isolated also because of his antifascism, he continued to paint magnificently during the 20s and the 30s. In 1943, while he was an evacuee in the countryside, weakened by sickness, his house, many paintings and all his cast of objects that had appeared in his works were lost in the only allied bombardment of Florence in WW2. Ghiglia died in 1945. Info gathered from: Oscar Ghiglia, Maestro del Novecento Italiano, published by Farsetti Arte in 1996. LISTEN BELOW FOR THE CORRECT PRONOUNCIATION OF HIS NAME
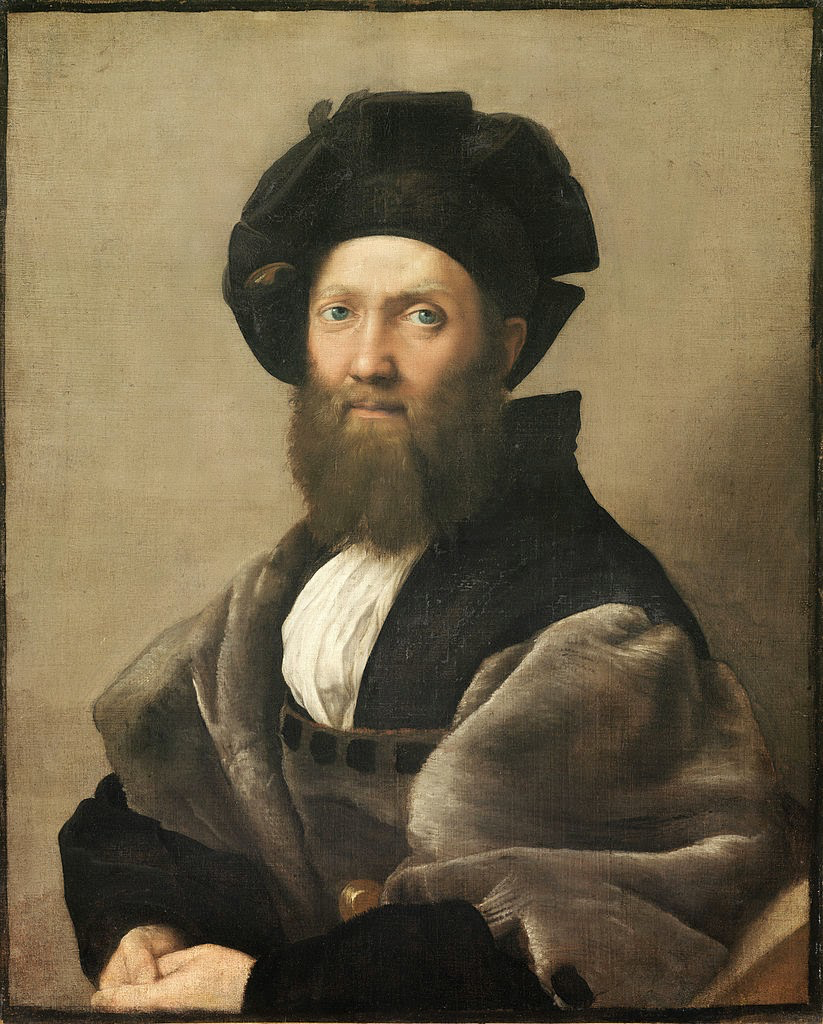
2 Comments
Sprezzatura is an Italian words but very few Italians nowadays would understand its meaning, although it sounds quite similar to "disprezzare" ( to despise) and "sprezzante"(contemptuous). The term was coined by Baldassarre Castiglione, an important character of Italian Renaissance, who was a political counsellor and the author of Il Cortigiano: a manual in which he outlines the characteristics of the perfect gentleman at court. The book, together with Macchiavelli's The Prince, marks an important shift in culture, when interest turns away from medieval metaphysics and turns to society. Il Cortigiano was one of the best-sellers of the century, and Francis I had it translated in French too. The book was written in Urbino between 1513 and 1524 and finally published in 1528, when in Italy courts such as the ones in Ferrara, Urbino, Mantua were at their peak. Courts were not only a centre of political power but cultural hubs where intellectuals, writers, poets, musicians and artists came together. In Il cortigiano, Castiglione talks about grace as the most important quality that a courtier should possess. The courtier is a gentleman who is supposed to know how to ride, lead a pleasant conversation, be a scholar, dance, dress up and have impeccable table manners as well as fighting skills. All these activities, says Castiglione, must be naturally performed without effort, and this is what sprezzatura means, a certain detachment and non-chalance that should dissimulate any strain; in Castiglione's words, make the viewer believe that one just can't go wrong. In the book he cites an example of a dancer who puts so much attention in what he does that he can be clearly seen counting his steps and is therefore an ungraceful and unpleasant partner. At the core of sprezzatura is not effortlessness though, but the ability at feigning it, the skill of dissimulating it. This is the other aspect of its influence on painting: bear in mind that the word "arte" in ancient Italian has the wider meaning of modus operandi, and it's at the root of words such as artifice. Sprezzatura is a behavioural quality of a painted sitter but the term can be also applied to the piece of art itself, made in a seemingly easy way and almost without thinking and with non-chalant virtuosism as if it sprang not from a long and arduous training and painstaking work but purely from natural flair. It was in those years that sprezzatura became a positive quality for the artist and nowadays we still hear the words "raw talent" enthusiastically spoken about as if the lack of effort or formal training was the most desirable characteristic. Roberto Calasso ( an Italian scholar) sees Tiepolo as a perfect example of an artist who practices sprezzatura: light and fluid touch, fast execution, confident and flamboyant brushwork.
|
Check the list below to see posts on these subjects.Categories
All
AuthorIlaria Rosselli Del Turco is an Italian painter living in London. |


















 RSS Feed
RSS Feed